[ad_1]
It’s no secret that the Ethereum community has been troubled by congestion and scalability points, inducing exorbitant fuel charges and different unfavorable person situations. Though these issues can’t be attributed to a single supply, two distinguished examples embrace elevated adoption and the utmost extractable worth (MEV) dynamic, enabling validators to arbitrarily exclude, embrace, and re-order transactions on the expense of customers. However, the truth that there are scalability points is kind of evident. Nevertheless, the million-dollar query is, how ought to we sort out these unfavorable situations? Properly, one, amongst a number of solutions to this query, is danksharding. However what’s danksharding, and the way does it work? These are two questions we got down to reply on this article. If this excites you, be a part of us as we dive deeper into the intricacies of danksharding!
Nevertheless, earlier than masking the ins and outs of danksharding, the article will lay the muse by masking the fundamentals of sharding usually. From there, we soar straight into the principle matter, introducing danksharding and the way it works. Then, to prime issues off, the article covers EIP-4844, also referred to as proto-danksharding.
What’s extra, in case you are already aware of the idea of danksharding, contemplate testing different Moralis content material right here on the Web3 weblog. For example, learn in regards to the intricacies of the Goerli testnet or discover ethers.js dapp growth. Additionally, you may discover ways to get all NFT transfers from any pockets utilizing Moralis’ NFT API! Plus, discover our tutorial on easy methods to get token metadata!
The aforementioned utility programming interface is certainly one of many Web3 APIs from Moralis. If you would like entry to all of them and revel in a considerably extra seamless developer expertise, enroll with Moralis now! Doing so is free, and with an account, you may absolutely leverage the facility of blockchain expertise!
What’s Sharding?
Centralized database administration generally makes use of the sharding method. Moreover, it refers to splitting an intensive database into much less important components or ”shards”. In doing so, builders can enhance effectivity and scalability by distributing a database throughout a number of machines working in parallel.
At any time when an utility or platform experiences elevated adoption, it usually will increase the quantity of saved knowledge. As you may think about, an overloaded database negatively impacts the efficiency of an utility/platform, harming the person expertise. Nevertheless, by sharding, it’s doable to alleviate a database’s overload to cut back redundant load time.
However, with a short overview of sharding usually, what does it entail in a Web3 context? The basic ideas stay the identical, and sharding a blockchain means splitting the community into distinct shards. Every shard is answerable for storing a portion of the chain’s knowledge and dealing with a singular subset of transactions. What’s extra, like sharding in conventional databases, it could actually probably enhance the community’s scalability and latency capabilities.
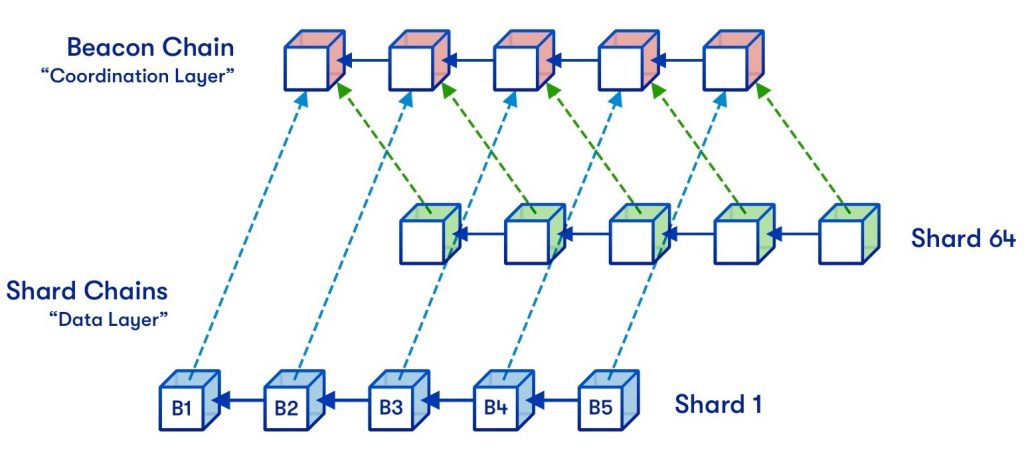
Furthermore, a typical idea you may wish to familiarize your self with is ”shard chains”. Shard chains are parts containing the fractions of the info that deal with the subset of transaction processing obligations. Briefly, shard chains are smaller blockchains working individually and independently from the principle community. Nevertheless, every shard chain submits a file to its fundamental chain at frequent intervals.
Since all shard chains have distinctive transaction histories and their very own set of nodes validating transactions, it’s doable to have numerous shard chains run concurrently. This will enhance community latency and increase throughput through parallel processing.
Now that you’ve a greater understanding of what sharding entails, each inside conventional growth and in a Web3 context, allow us to additional discover the issue sharding in blockchain networks goals to unravel within the subsequent part!
Why is Sharding in Blockchain Networks Obligatory?
In most blockchain networks, most nodes want to achieve a consensus to validate transactions. A downside of that is that the networks can solely course of a small variety of transactions concurrently. Furthermore, nodes are usually required to retailer all the historical past of a blockchain. That is very important to how blockchains akin to Bitcoin and Ethereum stay decentralized and might forestall fraudulent conduct. Nevertheless, with the notions of decentralization and excessive safety, these networks are compelled to sacrifice their scalability capabilities.
So, how are blockchain networks going to unravel these points with out going again on safety and decentralization? That is the place sharding enters the equation to alleviate this difficulty. Via sharding, nodes can forgo the requirement of downloading all the historical past of the chain and keep away from the necessity to validate all community transactions. Consequently, networks grow to be extra environment friendly and scalable, positively impacting the person expertise as demand will increase!
So, now that you’ve a extra profound understanding of what sharding is and why it will be important, allow us to dive into the central a part of this information and discover the intricacies of danksharding!
Danksharding Defined
Now that you’re extra aware of sharding usually, it’s time for the information’s fundamental matter: danksharding. So, what’s it? Danksharding is a more moderen sort of sharding structure proposed for the Ethereum community and will get its title from the researcher Dankrad Feist. This new design introduces some distinguished simplifications in comparison with earlier alternate options. In earlier sharding frameworks, the goal has usually been to extend the house for transactions. In distinction, danksharding takes a rollup-centric method by offering extra space for ”blobs” (extra on “blobs” under) of knowledge, which the Ethereum protocol itself doesn’t attempt to interpret.
”Blobs” is an abbreviation for ”binary giant objects”, and they’re usually fairly in depth. Nevertheless, they’re comparatively low-cost to transact with because the consensus layer shops them somewhat than Ethereum’s computation-heavy execution layer. Consequently, the computation layer doesn’t want to fret in regards to the particulars of the info. Moreover, it could actually as an alternative deal with the commitments of the info blobs.
Moreover, danksharding implements the ”merged price market” idea, which is likely one of the central underlying improvements behind this sharding design. Nevertheless, what does this imply, and the way does it work?
How Does Danksharding Work?
As touched on briefly, one of many central underlying revolutionary ideas behind danksharding is the merged price market; nonetheless, what does this imply? Properly, as an alternative of getting a specified variety of shards, every having its personal distinct blocks and block proposers, in danksharding, it’s a single proposer selecting all knowledge and all transactions that go into a specific slot.
Furthermore, to be able to make sure that the merged price market design doesn’t pressure important system necessities on validators, Ethereum launched ”proposer/builder separation”, or PBS. In a PBS-based system, a brand new specialised class of actors referred to as block builders bids for the proper to decide on the contents of a slot, and proposers solely want to decide on the legitimate header with the best bid. As such, solely the block builder is required to course of all the block; in the meantime, different customers and validators can confirm blocks extra effectively through knowledge availability sampling.
Via knowledge availability sampling, nodes can confirm bigger portions of knowledge by a pattern. Consequently, since nodes can keep away from processing all knowledge, the Ethereum community can deal with bigger portions of knowledge, offering a less expensive and quicker community extra suited to scaling and rollup optimization!
Nevertheless, danksharding is considerably difficult and comparatively complicated. As well as, because of this complexity, it could actually take fairly a while earlier than the Ethereum community is ripe for danksharding, which is the place EIP-4844 enters the image to introduce proto-danksharding!
What’s Proto-Danksharding? – EIP-4844
With the present state of Ethereum, many issues should be settled earlier than the community is able to undertake full danksharding. Right here is the place EIP-4844 enters the image – a proposal for implementing proto-danksharding. EIP stands for ”Ethereum Enchancment Proposal”, and EIP-4844 goals to implement a lot of the logic and lay the groundwork for full danksharding specs.
Nevertheless, the proposal doesn’t but embrace any precise implementation of sharding. Consequently, in proto-danksharding, validations and customers nonetheless must validate the provision of the entire knowledge immediately.
The proto-danksharding proposal’s most distinguished function is a brand new transaction sort: ”blob-carrying transactions”. These are fairly just like conventional transactions, solely that they carry an extra piece of knowledge blobs. Blobs are usually fairly in depth however may be cheaper than equal quantities of name knowledge. Furthermore, this knowledge sort shouldn’t be accessible for EVM (Ethereum Digital Machine) execution, and the digital machine can solely view commitments to those objects.
Since shoppers and validators are nonetheless required to obtain all the contents of the blobs, the bandwidth in proto-danksharding is aimed toward 1 MB/slot as an alternative of the overall 16 MB. Nevertheless, there are nonetheless important scalability features to be made because the knowledge shouldn’t be competing with the traditional fuel utilization of present blockchain transactions.
That briefly covers the intricacies of proto-danksharding/EIP-4844. Within the following part, we’ll evaluate proto-danksharding with EIP-4488, which is an earlier and simplified proposal aiming to unravel the identical difficulty.
What’s EIP-4488? – EIP-4844 vs EIP-4488
Now that you’ve familiarized your self with EIP-4844 (also referred to as proto-danksharding), allow us to take a more in-depth have a look at a considerably related enchancment protocol: EIP-4488. EIP-4488 is an earlier and extra simple try to unravel the identical difficulty. Nevertheless, this enchancment protocol goals to do it by the next two guidelines:
A restrict of 10 MB/block, plus an additional 300 bytes/transactionReducing name knowledge fuel prices from 16 fuel/byte to three fuel/byte
The exhausting restrict is likely one of the most simple strategies of guaranteeing {that a} important enhance within the common caseload doesn’t result in a rise in worse caseload. As such, EIP-4844 makes an attempt to cut back the fuel prices of name knowledge. Nevertheless, this can be a short-term answer that may show irrelevant if there was full sharding, as shards would make the most of blobs.
To briefly summarize, the principle distinction is that EIP-4844 aligns with all the sharding roadmap. In the meantime, EIP-4488 goals to unravel the difficulty in the intervening time. Nevertheless, this doesn’t imply we should understand the 2 enchancment protocols as trade-offs or aggressive. As proto-danksharding may take a while to implement because of engineering technicalities, EIP-4488 can assist resolve excessive prices utilizing rollups.
That covers this tutorial on danksharding. In case you have adopted alongside this far, you now hopefully know what danksharding is and the way it works. Within the subsequent part, we’ll present a short abstract together with different articles that you simply may discover fascinating!
Abstract – What’s Danksharding? – EIP-4844 and Danksharding Defined
Relating to the Web3 house, sharding refers back to the strategy of splitting up a blockchain into smaller ”shards”. Every shard is answerable for dealing with a portion of the chain’s transactions, together with storing a choice of its knowledge. Moreover, sharding can deliver many advantages, akin to elevated scalability and better throughput.
One sort of sharding methodology that has obtained an abundance of consideration these days is danksharding, which takes a rollup-centric method to sharding. Nevertheless, despite the fact that danksharding could be a legitimate answer to Ethereum’s scalability points sooner or later, the community shouldn’t be able to undertake this sharding design. However that is the place EIP-4844 or proto-danksharding enters the image!
Proto-danksharding is an EIP (Ethereum Enchancment Proposal) aiming to implement the elemental ideas and lay the groundwork for danksharding. The principle function of EIP-4844 is a brand new transaction sort known as blob-carrying transactions. Nevertheless, proto-danksharding nonetheless requires validators and shoppers to obtain all the contents of the blobs. As such, bandwidth is considerably restricted and aimed toward 1 MB/slot. Nevertheless, it nonetheless presents alternatives for important scalability features.
However, when you discovered this tutorial on danksharding useful, contemplate studying different articles right here on the Moralis weblog. For example, try our tutorial on Web3 py and discover Ethereum Python implementation. As well as, discover ways to take heed to good contact occasions utilizing ethers.js or learn up on the Sepolia testnet!
What’s extra, if you wish to grow to be a more adept Web3 developer, enroll in Moralis Academy at this time! The academy presents industry-leading blockchain programs for each new and extra skilled builders. For example, study the fundamentals with the course on Ethereum fundamentals.
Lastly, bear in mind to enroll with Moralis to entry a extra seamless workflow for all of your future blockchain growth endeavors!
[ad_2]
Source link





