[ad_1]
This good contract programming tutorial will train you the right way to incorporate current good contract performance into your dapps. Due to wagmi and Moralis – the instruments we use on this tutorial – your dapp will be capable of set off “learn” and “write” Web3 contract strategies or features. The next snippets of code will do all of the heavy lifting:
To run “learn” good contract features:const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.utils.runContractFunction({
abi,
functionName,
tackle,
chain,
}); To run “write” good contract features:const { config } = usePrepareContractWrite({})const { write } = useContractWrite()
Alongside the way in which, you’ll even have an opportunity to discover ways to get a pockets’s ERC20 token stability. That is the place Moralis’ Ethereum API for tokens will do the trick by way of the next snippet of code:
const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getWalletTokenBalances({
tackle,
chain,
});
In the event you’re already a proficient developer accustomed to Moralis, go forward and implement the above code snippets instantly! If not, be certain to finish in the present day’s good contract programming tutorial and degree up your recreation. Simply create your free Moralis account and observe our lead!

Overview
The core of in the present day’s article shall be our good contract programming tutorial. The latter will include two sub-tutorials – one educating you to run “learn” good contract features and the opposite to run “write” features. In the event you’d like to start the tutorial instantly, click on right here.
For in the present day’s tutorial, your JavaScript (NodeJS and ReactJS) proficiency will get you to the end line. Understand that we’ll offer you the first strains of code herein and hyperlinks to the entire code that awaits you on GitHub. Consequently, we’ve ensured that there aren’t any obstacles in your manner and that you would be able to simply full this good contract programming tutorial.
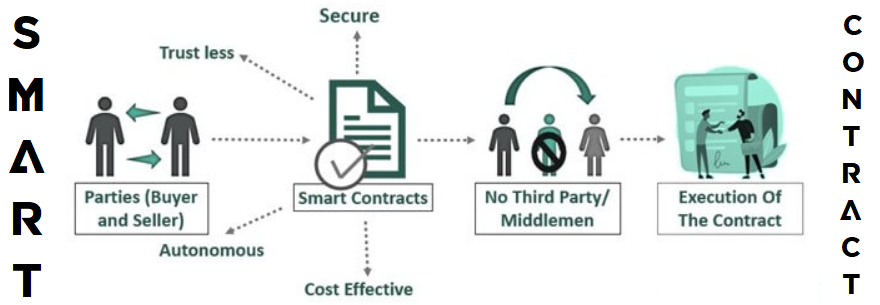
After you’ve rolled up your sleeves and efficiently accomplished the tutorial, we’re going to offer you some fundamentals associated to good contract programming. As such, we’ll clarify what good contracts are and what good contract programming is. We’ll additionally listing the main good contract programming languages in case a few of you need to begin creating your personal good contracts.
In the event you’d wish to increase your abilities even additional after in the present day, be certain to take a look at Moralis Academy and enroll within the Ethereum Good Contract Programming 101 course!
Good Contract Programming Tutorial
As you proceed, you’ll have a possibility to finish two sub-tutorials. One will present you the right way to run good contract features out of your dapp, and the opposite the right way to write them. The primary sub-tutorial will give attention to finishing the duty inside your terminal, with out truly making a frontend dapp. Nonetheless, the second good contract programming tutorial may even present you the right way to create a easy frontend dapp. Right here’s the gist of that dapp:
The above screenshot reveals that the dapp you’ll have an opportunity to construct within the second sub-tutorial allows customers to attach their wallets. As soon as customers join their wallets, they get to ship their Chainlink (LINK) tokens by getting into the quantity and pasting a recipient tackle:
As a way to incorporate current good contracts in dapps, you additionally need to discover ways to discover their particulars. That is the place blockchain explorers enter the image. Since we’ll be specializing in the Ethereum and Polygon (Mumbai) chains, Etherscan and PolygonScan will do the trick. Happily, each of those explorers are fairly related. Basically, it’s essential to enter a wise contract’s tackle or undertaking’s/token’s identify. Then, you scroll down the place you see a menu bar and click on on the “Contract” possibility. By doing so, you’ll get to discover a wise contract’s code, together with the ABI (by way of “Code”), and the contract’s “learn” and “write” features (by way of “Learn Contract” and “Write Contract”):
You should even have your Moralis Web3 API key to finish the upcoming challenges. To get it, be certain to create your free Moralis account. Then, you’ll be able to entry your admin space and procure your API key:
Run Good Contract Capabilities
One of many methods to include good contracts into dapps is to run good contract features. Due to Moralis’ “runContractFunction” endpoint, it turns into extremely simple. You simply have to create a NodeJS dapp and incorporate the right endpoint.
Begin by making a “ContractFunctions” folder and open it in Visible Studio Code (VSC). Subsequent, use your terminal to initialize NodeJS by working the next command:
npm init -y
The above command will lead to a “bundle.json” file in your file tree:
Then, set up the required dependencies with this command:
npm i moralis dotenv
Additionally, create your “.env” file, by which it’s essential to paste your above-obtained Web3 API key:
Transferring ahead, create an “index.js” file. The latter will include the logic required to finish this good contract programming tutorial. Open this file, and on the prime, import Moralis and require “.env”:
const Moralis = require(“moralis”).default;
require(“dotenv”).config();
Then it’s essential to outline the ABI of the good contract that you just need to give attention to. We’ll use the “Cool Cats” contract on the Ethereum chain. Through the use of the information offered within the earlier part, you already know the right way to get any contract’s ABI:
With the ABI copied, return to VSC and create a brand new “abi.json” file. Open it and paste the contract’s ABI. Subsequent, use “Shift+Choice+F” on Mac (or Home windows/Linux equal) to correctly rearrange the content material. This contract has a number of “learn” features; nonetheless, we are going to give attention to working “getPrice” with the “runContractFunction” endpoint.
Using the “runContractFunction” Technique
Reopen your “index.js” file and require the above-created “abi.json” file:
const ABI = require(“./abi.json”);
You may then initialize Moralis by using your API key and implementing the “Moralis.EvmApi.utils.runContractFunction” methodology. You additionally want to make use of the good contract’s particulars as parameters. When specializing in “Cool Cats”, these are the strains of code that do the trick:
Moralis.begin({
apiKey: course of.env.MORALIS_KEY
}).then(async()=>{
const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.utils.runContractFunction({
tackle: “0x1A92f7381B9F03921564a437210bB9396471050C”,
functionName: “getPrice”
abi: ABI
});
console.log(response.uncooked)
})
Lastly, you’ll be able to run your “index.js” script with the next command:
node index.js
In case you have adopted our lead to this point, your terminal ought to return the next outcomes:
Be aware: The costs in ETH use 18 decimal locations. Therefore, the above end result signifies that the preliminary value for the “Cool Cats” NFT was 0.02 ETH.
You could find the video model of this sub-tutorial beneath. That is additionally the place you’ll be able to apply working good contract features on one other “learn” perform (“tokenURI“). As well as, you should utilize the video beneath to discover ways to mix the outcomes of working the “getPrice” perform with Moralis’ “getNFTLowestPrice” NFT API endpoint.
Write Good Contract Capabilities
When working “learn” good contract features, you don’t change the state of the blockchain (you don’t execute on-chain transactions). Nonetheless, whenever you write good contract features, you execute blockchain transactions. Thus, it’s essential to have your MetaMask pockets prepared for this good contract programming tutorial. Transferring ahead, we’ll give attention to an instance good contract dapp that runs on the Polygon testnet (Mumbai). We’ll stroll you thru the core elements of the backend and frontend scripts of our instance “Ship ChainLink” dapp.
Be aware: You could find the entire code behind our instance dapp on GitHub. There you’ll see the “write” (frontend) and “backend” folders.
With our code cloned, be sure to have the content material of the “write” folder in your “frontend” folder. Then, open that folder in VSC and set up the required dependencies with this command:
npm i
Contained in the “index.js” frontend script, you’ll be able to see all required functionalities imported on the prime, together with wagmi:
import React from ‘react’;
import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom/consumer’;
import ‘./index.css’;
import App from ‘./App’;
import { configureChains, mainnet, WagmiConfig, createClient } from ‘wagmi’
import { publicProvider } from ‘wagmi/suppliers/public’
import { polygonMumbai } from ‘@wagmi/chains’;
Subsequent, this script allows the Mumbai chain:
const { supplier, webSocketProvider } = configureChains(
[mainnet, polygonMumbai],
[publicProvider()],
)
That is the place we create a wagmi consumer:
const consumer = createClient({
autoConnect: true,
supplier,
webSocketProvider,
})
Lastly, this script wraps all the app in “wagmiConfig”:
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(doc.getElementById(‘root’));
root.render(
<WagmiConfig consumer={consumer}>
<App />
</WagmiConfig>
);
Implementing the MetaMask Pockets Connector
With the strains of code above, you’ve arrange your frontend. Subsequent, you should utilize wagmi to attach the MetaMask pockets to your dapp contained in the “App.js” script. For an in depth code walkthrough, use the video beneath, beginning at 5:03. Nonetheless, so far as connecting pockets performance goes, the next “import” strains are a prerequisite:
import { useConnect, useAccount, usePrepareContractWrite, useContractWrite } from “wagmi”;
import { MetaMaskConnector } from “wagmi/connectors/metaMask”;
import { useEffect, useState } from “react”;
The next strains of code contained in the “App()” perform finalizes the method:
const { tackle, isConnected } = useAccount();
const { join } = useConnect({
connector: new MetaMaskConnector(),
});
Getting the Pockets Stability
One of many code snippets from this text’s introduction focuses on getting a pockets stability. To implement this characteristic, you will need to use the “backend” folder. In it, you’ll find the backend “index.js” script (08:15). This script solely comprises one endpoint: “/getBalance“. On the core of this endpoint is the “Moralis.EvmApi.token.getWalletTokenBalances” methodology. The latter fetches the linked pockets tackle by way of “question.tackle” for the LINK token (by way of “tokenAddresses“) on the Mumbai chain (by way of chain ID). Listed here are the strains of code for this:
const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getWalletTokenBalances({
tackle: question.tackle,
chain: “80001”,
tokenAddresses: [“0x326C977E6efc84E512bB9C30f76E30c160eD06FB”]
})
Identical to you probably did within the above “run” good contract programming tutorial, you will need to initialize Moralis along with your API key:
Moralis.begin({
apiKey: course of.env.MORALIS_KEY,
}).then(() => {
app.pay attention(port, () => {
console.log(`Listening for reqs`);
});
});
Be aware: Once more, be certain to retailer your key inside your “.env” file.
Don’t forget to “cd” into your “backend” folder and set up all required dependencies with the “npm i” command. Then, you’ll be capable of run your backend dapp with the next command:
node index.js
Along with your backend working, your frontend (App.js) will get to show the stability with the next “async” perform:
async perform getBalance() {
const response = await axios.get(“http://localhost:3000/getBalance”, {
params: {
tackle: tackle,
},
});
setUserBal(response.information.stability);
}
The script makes use of “useEffect” to name the above “getBalance” perform when wallets hook up with our dapp. Ensure that to open a brand new terminal in your frontend as a result of it’s essential to maintain your backend working. Then, “cd” into your “frontend” folder and run the next command:
npm run begin
Be aware: Use the video beneath (14:10) to discover how your dapp’s enter fields work.
The “write” Operate
With the above functionalities in place, we’ve reached the core side of this good contract programming tutorial. That is the place we’ll take a more in-depth take a look at the strains of code that allow your dapp to set off a wise contract’s “write” features.
As you might need seen earlier, the “App.js” script imports “usePrepareContractWrite” and “useContractWrite“. This allows your code to organize the information and truly set off the “write” contract features. Utilizing the video beneath, beginning at 16:00, you’ll be able to see how we use PolygonScan to get the “ChainLink Token” good contract particulars. This consists of inspecting all “write” features this good contract consists of and copying its ABI. You have already got the latter prepared within the “abi.json” file. Now, since our dapp goals to switch LINK tokens, we need to give attention to the “switch” perform of the “ChainLink Token” contract.
Be aware: You may study the aim of the “useDebounce.js” script within the video beneath (17:27).
In the end, the “App.js” script first prepares the small print of the contract we’re specializing in by using “usePrepareContractWrite“. Then, it makes use of “useContractWrite” based mostly on these particulars. These are the strains of code that allow our instance dapp to set off a “write” good contract perform:
const { config } = usePrepareContractWrite({
tackle: ‘0x326C977E6efc84E512bB9C30f76E30c160eD06FB’,
abi: ABI,
chainId: 80001,
functionName: ‘switch(tackle,uint256)’,
args: [debouncedReceiver, debouncedSendAmount],
enabled: Boolean(debouncedSendAmount)
})
const { write } = useContractWrite(config)
The above “write” perform is triggered when customers hit the “Ship” button:
<button disabled={!write} onClick={()=>write?.()}>Ship</button>
Lastly, right here’s the video that we’ve been referencing on this second sub-tutorial:
What are Good Contracts?
Good contracts are on-chain packages – items of software program that run on improvement blockchains (e.g., Ethereum). As such, good contracts automate and information on-chain processes. They achieve this by executing particular predefined actions each time sure predefined situations are met. It’s due to this automation that these on-chain packages are “good”. Moreover, good contracts are cost-effective, autonomous, trustless, and safe. Plus, the code behind each good contract is absolutely clear – everybody can view it with blockchain explorers.
Thanks to those properties, Web3 contracts have monumental potential to seriously change all industries within the upcoming years. They’ve the facility to remove intermediaries and make the world extra environment friendly and truthful. In fact, that’s the long-term purpose. Nonetheless, Web3 remains to be in its early stage; subsequently, now’s the perfect time to study Web3 programming. What higher manner to do this than to tackle a wise contract programming tutorial?
What’s Good Contract Programming?
So, what is wise contract programming? At its core, good contract programming is the method of writing, compiling, deploying, and verifying good contracts. Nonetheless, because the first half – writing a wise contract – is the trickiest, good contract programming primarily focuses on that process. In spite of everything, you’ll be able to compile, deploy, and confirm Web3 contracts with a few clicks when utilizing the precise instruments. Then again, writing a correct good contract from scratch is a somewhat superior feat, particularly for those who intention to implement some authentic functionalities.
To create a wise contract, it’s essential to be proficient in one of many programming languages for good contracts. Furthermore, there isn’t one common good contract language that targets all well-liked blockchains, at the least not but. As an alternative, it’s essential to determine which blockchain you need to give attention to after which select among the many supported languages for that chain. All in all, if you wish to grasp good contract programming, it’s essential to be ready to place in fairly some effort and time.
Nonetheless, to start out working with good contracts is somewhat easy. For example, if you wish to deploy your good contract on Ethereum that offers with already identified duties, you should utilize one in all many verified good contract templates and apply minor tweaks. Then, you’ll be able to compile, deploy, and confirm it with the Remix IDE and MetaMask. Moreover, you can begin incorporating good contract functionalities into decentralized functions (dapps). An awesome instance of that might be to name a wise contract perform from JavaScript. You should use a Web3 JS name contract perform or hearken to good contract occasions utilizing ethers.js.

Languages for Good Contract Programming
Under, you’ll be able to see the listing of the six hottest good contract coding languages and the main chains they give attention to:
Solidity for Ethereum and different EVM-compatible chainsVyper for Ethereum and different EVM-compatible chainsYul (and Yul+) as an intermediate language for the Solidity compiler Rust for Solana, Polkadot, NEAR, and a number of other different chainsC++ for EOSJavaScript (NodeJS) for Hyperledger Cloth and NEAR
Different note-worthy programming languages that you should utilize to jot down good contracts embody Readability (Bitcoin), Golang/Go (Ethereum), Marlowe (Cardano), Cadence (Circulation), LIGO (Tezos), Transfer (Aptos), TEAL (Algorand), and Python (Hyperledger Cloth).
Be aware: If you wish to study extra particulars about Solidity, Vyper, and Yul, be certain to make use of the “programming languages for good contracts” hyperlink above.
With regards to incorporating good contract functionalities into dapps, you should utilize any of your favourite programming languages due to Moralis’ cross-platform interoperability.
Good Contract Programming Tutorial for Blockchain Builders – Abstract
In in the present day’s good contract programming tutorial, we lined fairly some floor. You had an opportunity to observe our lead and full in the present day’s good contract programming tutorial. First, you realized to create a NodeJS dapp that runs “learn” good contract features utilizing the Moralis “runContractFunction” endpoint. And within the second tutorial, you had a possibility to clone our dapp and use it to set off “write” good contract features. As soon as we completed the tutorial, we addressed a few of the fundamentals. As such, you had an opportunity to refresh your understanding of good contracts and good contract programming. You additionally realized what the main good contract coding languages are.
In the event you loved in the present day’s tutorial, be certain to dive into Moralis’ docs and sort out the “Tutorials” part. Don’t overlook to bolster your blockchain improvement data by visiting the Moralis YouTube channel and the Moralis weblog. These two retailers cowl a variety of matters. For example, a few of the newest articles will show you how to perceive blockchain-based information storage, the right way to get contract logs, the right way to get Ethereum transaction particulars, and rather more. If you wish to tackle the good contract programming course talked about within the “Overview” part, be certain to enroll in Moralis Academy.
[ad_2]
Source link





