[ad_1]
Constructing a decentralized cryptocurrency change may appear fairly cumbersome. Nonetheless, you may really create a DEX in about 90 minutes in the event you depend on the best instruments. If you happen to comply with alongside on this article’s tutorial, you’ll use React, NodeJS, and two Web3 instruments which might be the spine of at present’s article: the Moralis Web3 Information API and the 1inch aggregator. Thanks to those instruments, you may discover ways to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change with out breaking a sweat! Now, let’s have a look at the core code snippets that may make it easier to fetch costs of two crypto belongings concerned in a swap:
const responseOne = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getTokenPrice({
handle: question.addressOne
})
const responseTwo = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getTokenPrice({
handle: question.addressTwo
})
So far as the precise change performance goes, the 1inch API allows you to implement it with the next strains of code:
const allowance = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/approve/allowance?tokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}&walletAddress=${handle}`)
const approve = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/approve/transaction?tokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}`)
const tx = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/swap?fromTokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}&toTokenAddress=${tokenTwo.handle}&quantity=${tokenOneAmount.padEnd(tokenOne.decimals+tokenOneAmount.size, ‘0’)}&fromAddress=${handle}&slippage=${slippage}`)
In case you are enthusiastic about studying learn how to implement the above snippets of code, create your free Moralis account and dive into the tutorial on learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change under!

Overview
The primary a part of at present’s article is all about exhibiting you learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change. That is the place you may comply with our lead, use our code snippets, and create the backend and frontend parts of your DEX dapp.
Under the tutorial, you may meet up with the idea behind at present’s subject and get your fundamentals of constructing a DEX for cryptocurrencies so as. That is the place we’ll clarify what a decentralized change (DEX) is, the way it works, and the way it compares to a centralized change. We’ll additionally look at the instruments you want when constructing a decentralized cryptocurrency change.

Tutorial: Easy methods to Construct a Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate
On this tutorial, you’ll mix your JavaScript proficiency with the facility of Moralis and the 1inch aggregator to construct your individual occasion of our instance cryptocurrency DEX. To make the method as simple as attainable, we determined to interrupt it down into a number of phases and substages. First, we’ll stroll you thru the preliminary venture setup. Then, we’ll present you learn how to construct your decentralized cryptocurrency change’s header. Subsequent, we’ll deal with making a swap web page, which would be the frontend of all exchange-related functionalities. With the frontend in place, we’ll information you thru the method of implementing your backend of the crypto change. That is the place you’ll lastly discover ways to implement the above-outlined snippets of code.
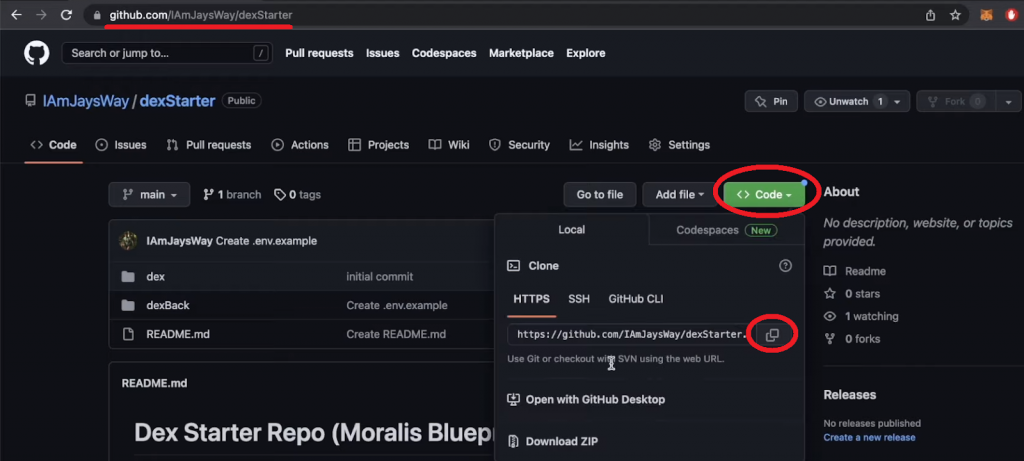
Setting Up Your Challenge
As an alternative of ranging from scratch, go to the “dexStarter” GitHub repo and duplicate the URL handle as proven within the picture above. By cloning our code, you don’t have to fret about styling and can be capable to commit your most consideration to implementing Web3 performance.
After copying the above GitHub URL, open a brand new venture in Visible Studio Code (VSC). Then, use VSC’s terminal to clone the code with this command:
git clone https://github.com/IAmJaysWay/dexStarter
Subsequent, entry the “dexStarter” folder manually or use the “cd dexStarter” command. Contained in the folder, you may see the “dex” and “dexBack” folders. The previous holds the frontend parts and the latter the backend scripts. By cloning our code, you’re beginning with easy React and NodeJS apps. To make them work correctly, you’ll want to set up all of the required dependencies. Beginning with the frontend, “cd” into “dex” and enter the next command that may set up all of the frontend dependencies:
npm set up
With the dependencies in place, you can begin your React app:
npm run begin
If you happen to go to “localhost:3000”, you will notice this:
Constructing the Header of the Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate
From the “dex/src” folder, open “App.js” and import the “Header.js” part on the high:
import Header from “./parts/Header”;
Subsequent, use that part in your “App” operate:
operate App() {
return (
<div className=”App”>
<Header />
</div>
)
}
Then, go to “dex/src/parts” and open the “Header.js” file so as to add a brand, web page choices, and the “Join” button. On the high of the script, import the brand and icon pictures:
import Emblem from “../moralis-logo.svg”;
import Eth from “../eth.svg”;
Add the next strains of code to make sure that the “Header” operate shows the brand, web page choices, and the “Join” button:
operate Header(props) {
const {handle, isConnected, join} = props;
return (
<header>
<div className=”leftH”>
<img src={Emblem} alt=”brand” className=”brand” />
<div className=”headerItem”>Swap</div>
<div className=”headerItem”>Tokens</div>
</div>
<div className=”rightH”>
<div className=”headerItem”>
<img src={Eth} alt=”eth” className=”eth” />
Ethereum
</div>
<div className=”connectButton” onClick={join}>
{isConnected ? (handle.slice(0,4) +”…” +handle.slice(38)) : “Join”}
</div>
</div>
</header>
);
}
With the above additions to “App.js” and “Header.js”, your frontend ought to mirror these adjustments:
Transferring on, you’ll want to activate the “Swap” and “Tokens” choices. To take action, return to “App.js” and import “Swap”, “Tokens”, and “Routes”:
import Swap from “./parts/Swap”;
import Tokens from “./parts/Tokens”;
import { Routes, Route } from “react-router-dom”;
Subsequent, deal with the “Header” div, the place you’ll want to add a “mainWindow” div with the right routes:
<Header join={join} isConnected={isConnected} handle={handle} />
<div className=”mainWindow”>
<Routes>
<Route path=”/” ingredient={<Swap isConnected={isConnected} handle={handle} />} />
<Route path=”/tokens” ingredient={<Tokens />} />
</Routes>
</div>
Return to “Header.js” and import “Hyperlink”:
import { Hyperlink } from “react-router-dom”;
You additionally must wrap your “Swap” and “Tokens” divs of their hyperlink parts:
<Hyperlink to=”/” className=”hyperlink”>
<div className=”headerItem”>Swap</div>
</Hyperlink>
<Hyperlink to=”/tokens” className=”hyperlink”>
<div className=”headerItem”>Tokens</div>
</Hyperlink>
Now, the “Swap” and “Token” choices take you to their matching routes:
Creating the Swap Web page
Open “Swap.js” and import a number of Ant Design UI framework parts:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from “react”;
import { Enter, Popover, Radio, Modal, message } from “antd”;
import {
ArrowDownOutlined,
DownOutlined,
SettingOutlined,
} from “@ant-design/icons”;
Then, deal with the “Swap” operate the place you need to add a “tradeBox” div. By using Ant Design, it’s simple to incorporate a slippage setting choice:
operate Swap() {
const [slippage, setSlippage] = useState(2.5);
operate handleSlippageChange(e) {
setSlippage(e.goal.worth);
}
const settings = (
<>
<div>Slippage Tolerance</div>
<div>
<Radio.Group worth={slippage} onChange={handleSlippageChange}>
<Radio.Button worth={0.5}>0.5%</Radio.Button>
<Radio.Button worth={2.5}>2.5%</Radio.Button>
<Radio.Button worth={5}>5.0%</Radio.Button>
</Radio.Group>
</div>
</>
);
return (
<div className=”tradeBox”>
<div className=”tradeBoxHeader”>
<h4>Swap</h4>
<Popover
content material={settings}
title=”Settings”
set off=”click on”
placement=”bottomRight”
>
<SettingOutlined className=”cog” />
</Popover>
</div>
</div>
</>
);
}
On account of the above strains of code, your “Swap” web page ought to have a “Swap” body with a gear icon that opens the slippage tolerance setting:
Including Alternate Enter Fields
Your change should embody correct enter fields if you wish to swap tokens. These fields ought to enable customers to pick the tokens they need to swap and their quantities. Therefore, you’ll want to apply some tweaks to your “tradeBox” div. So, create an “inputs” div under the “tradeBoxHeader” div:
<div className=”inputs”>
<Enter
placeholder=”0″
worth={tokenOneAmount}
onChange={changeAmount}
disabled={!costs}
/>
<Enter placeholder=”0″ worth={tokenTwoAmount} disabled={true} />
<div className=”switchButton” onClick={switchTokens}>
<ArrowDownOutlined className=”switchArrow” />
</div>
<div className=”assetOne” onClick={() => openModal(1)}>
<img src={tokenOne.img} alt=”assetOneLogo” className=”assetLogo” />
{tokenOne.ticker}
<DownOutlined />
</div>
<div className=”assetTwo” onClick={() => openModal(2)}>
<img src={tokenTwo.img} alt=”assetOneLogo” className=”assetLogo” />
{tokenTwo.ticker}
<DownOutlined />
</div>
You additionally want so as to add acceptable state variables. So, add the next strains under the “Slippage” state variable:
const [tokenOneAmount, setTokenOneAmount] = useState(null);
const [tokenTwoAmount, setTokenTwoAmount] = useState(null);
const [tokenOne, setTokenOne] = useState(tokenList[0]);
const [tokenTwo, setTokenTwo] = useState(tokenList[1]);
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState(false);
const [changeToken, setChangeToken] = useState(1);
Subsequent, add correct capabilities to deal with the altering of quantities of tokens and the “from/to” switching of the tokens. Add the next snippets of code under the “handleSlippageChange” operate:
operate changeAmount(e) {
setTokenOneAmount(e.goal.worth);
if(e.goal.worth && costs){
setTokenTwoAmount((e.goal.worth * costs.ratio).toFixed(2))
}else{
setTokenTwoAmount(null);
}
}
operate switchTokens() {
setPrices(null);
setTokenOneAmount(null);
setTokenTwoAmount(null);
const one = tokenOne;
const two = tokenTwo;
setTokenOne(two);
setTokenTwo(one);
fetchPrices(two.handle, one.handle);
}
To supply a correct choice of tokens, you want an excellent record. Luckily, you should utilize our “tokenList.json” file for that objective. The latter is principally an array of tokens that features tickers, icons, names, addresses, and decimals:
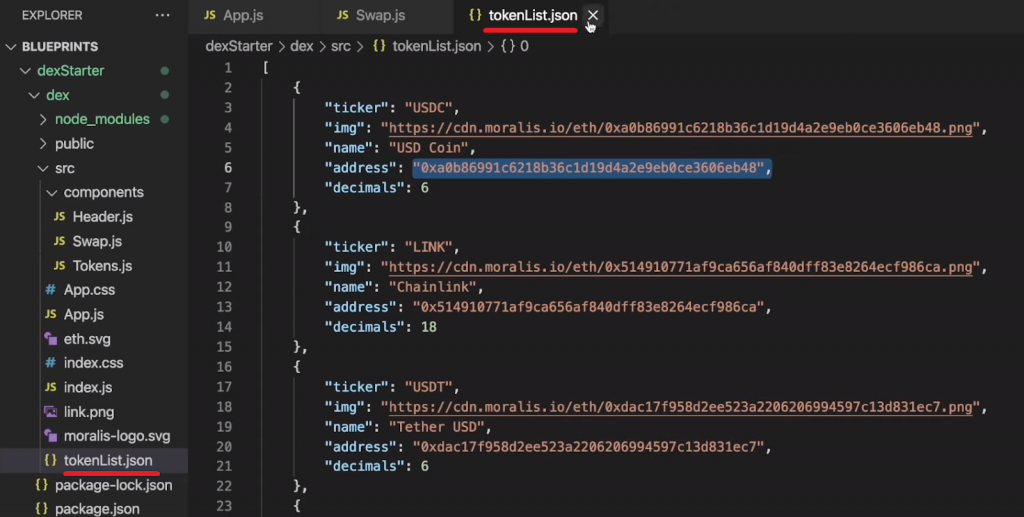
So, add the next line below the present imports inside “Swap.js”:
import tokenList from “../tokenList.json”;
Including Token Choice Modals
You most likely observed that the above-implemented “inputs” div contains two “openModal” capabilities. In an effort to make these capabilities work, you’ll want to equip your “tradeBox” div on the high of “return” with the next strains:
return (
<>
{contextHolder}
<Modal
open={isOpen}
footer={null}
onCancel={() => setIsOpen(false)}
title=”Choose a token”
>
<div className=”modalContent”>
{tokenList?.map((e, i) => {
return (
<div
className=”tokenChoice”
key={i}
onClick={() => modifyToken(i)}
>
<img src={e.img} alt={e.ticker} className=”tokenLogo” />
<div className=”tokenChoiceNames”>
<div className=”tokenName”>{e.title}</div>
<div className=”tokenTicker”>{e.ticker}</div>
</div>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</Modal>
Additionally, be sure you add the “openModal” and “modifyToken” capabilities as effectively:
operate openModal(asset) {
setChangeToken(asset);
setIsOpen(true);
}
operate modifyToken(i){
setPrices(null);
setTokenOneAmount(null);
setTokenTwoAmount(null);
if (changeToken === 1) {
setTokenOne(tokenList[i]);
fetchPrices(tokenList[i].handle, tokenTwo.handle)
} else {
setTokenTwo(tokenList[i]);
fetchPrices(tokenOne.handle, tokenList[i].handle)
}
setIsOpen(false);
}
To finish the “Swap” web page, add the “Swap” button. You are able to do this by including the next line of code under the “inputs” div:
<div className=”swapButton” disabled= !isConnected onClick={fetchDexSwap}>Swap</div>
If you happen to efficiently applied all the above, it is best to have your “Swap” web page prepared:
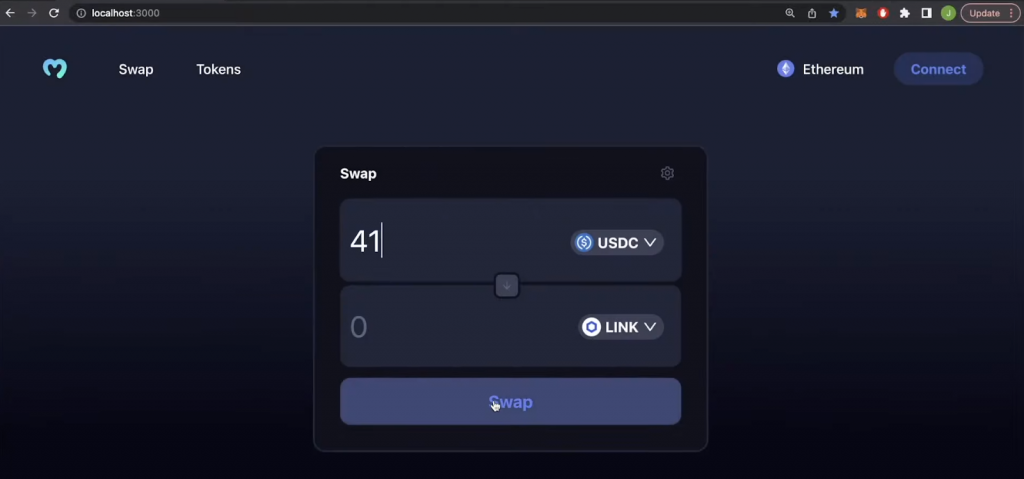
With the frontend below your belt, it’s time to implement the backend performance. For the reason that backend is the primary focus of at present’s article, that is the place you’ll lastly discover ways to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change.
Construct a Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate
Earlier than transferring ahead, receive your Moralis Web3 API key. To take action, create your free Moralis account. Together with your account up and working, you’ll be capable to entry your admin space. From there, you get to repeat your API key in two clicks:
Subsequent, paste your key into the “.env.instance” file that awaits you contained in the “dexBack” folder. Then, rename that file to “.env”.
The core of your NodeJS backend dapp is the “index.js” script. That is the file you’ll want to tweak to fetch token costs. Nonetheless, first, use a brand new terminal and “cd” into the “dexBack” folder. Then, set up the backend dependencies by getting into the “npm set up” command.
With the dependencies in place, open “index.js” and implement the “getTokenPrice” strains of code from the intro. Moreover, you’ll want to replace the “app.get” operate, which fetches token costs in USD and supplies them to the “/tokenPrice” endpoint:
app.get(“/tokenPrice”, async (req, res) => {
const {question} = req;
const responseOne = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getTokenPrice({
handle: question.addressOne
})
const responseTwo = await Moralis.EvmApi.token.getTokenPrice({
handle: question.addressTwo
})
const usdPrices = {
tokenOne: responseOne.uncooked.usdPrice,
tokenTwo: responseTwo.uncooked.usdPrice,
ratio: responseOne.uncooked.usdPrice/responseTwo.uncooked.usdPrice
}
return res.standing(200).json(usdPrices);
});
With the above strains of code in place, save your “index.js” file, and run your backend with the next command:
node index.js
Notice: The ultimate “index.js” backend file is on the market on GitHub.
Getting Token Costs to the Frontend
At this level of the “learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change” feat, we’ll deal with getting token costs from the above-presented backend to the “Swap” web page. As such, you’ll want to refocus on the “swap.js” file. Under the present imports, import Axios – a NodeJS promise-based HTTP shopper:
import axios from “axios”;
Then, go to the a part of “swap.js” the place different state variables are positioned and add the next:
const [prices, setPrices] = useState(null);
To fetch the costs out of your backend, you need to additionally add the “fetchPrices” async operate under the “modifyToken” operate:
async operate fetchPrices(one, two){
const res = await axios.get(`http://localhost:3001/tokenPrice`, {
params: {addressOne: one, addressTwo: two}
})
setPrices(res.information)
}
Under the “fetchPrices” operate, additionally add a corresponding “useEffect”:
useEffect(()=>{
fetchPrices(tokenList[0].handle, tokenList[1].handle)
}, [])
When you implement the above strains of code, your “Swap” field will be capable to use token costs and their ratios. As such, as soon as customers enter the quantity of the primary token, it should mechanically populate the quantity of the opposite token:
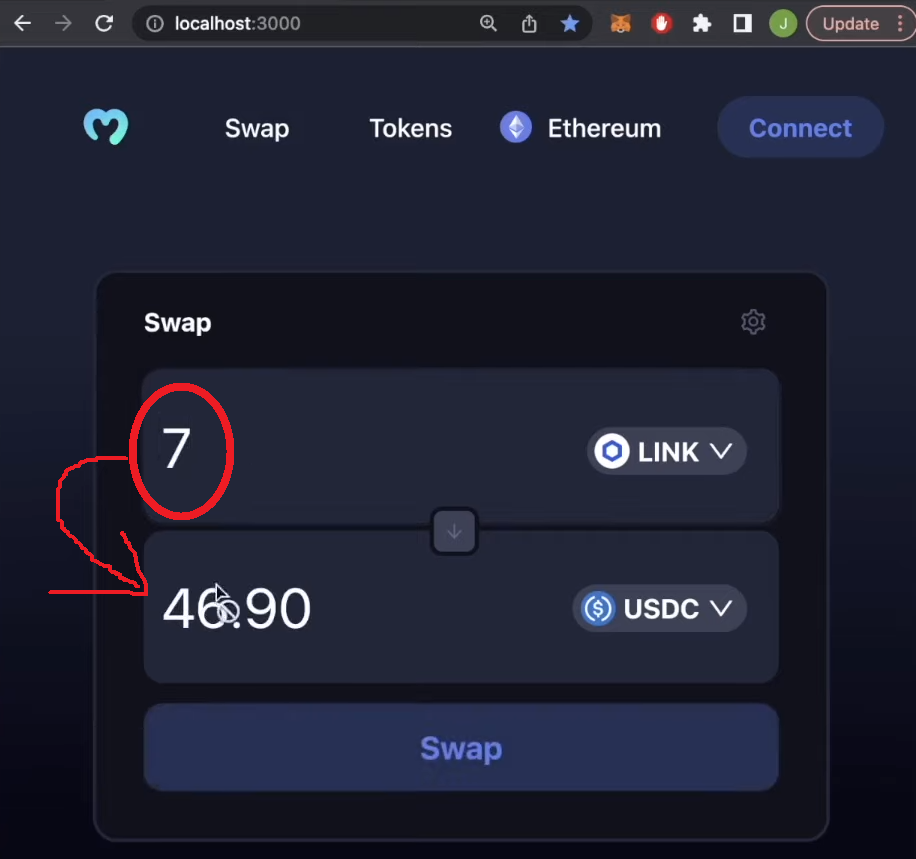
Web3 Authentication: Connecting MetaMask
Your decentralized change is coming alongside properly; nevertheless, its “Join” button continues to be inactive. Luckily, you should utilize the wagmi library so as to add the required Web3 login performance. To that finish, open your frontend “index.js” file positioned within the “dex/src” folder. On the high of that script, import a number of wagmi parts and a public supplier under the present imports:
import { configureChains, mainnet, WagmiConfig, createClient } from “wagmi”;
import { publicProvider } from “wagmi/suppliers/public”;
Then, you’ll want to configure the chains and create a shopper. You are able to do that by including the next code snippet under the above imports:
const { supplier, webSocketProvider } = configureChains(
[mainnet],
[publicProvider()]
);
const shopper = createClient({
autoConnect: true,
supplier,
webSocketProvider,
});
Subsequent, wrap your app with “WagmiConfig”:
<React.StrictMode>
<WagmiConfig shopper={shopper}>
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
</WagmiConfig>
</React.StrictMode>
Notice: The ultimate frontend “index.js” script awaits you on GitHub.
To make sure that the “Join” button does its factor, reopen “App.js” and import the MetaMask connector and wagmi parts under the present imports:
import { useConnect, useAccount } from “wagmi”;
import { MetaMaskConnector } from “wagmi/connectors/metaMask”;
Subsequent, add the next strains of code contained in the “App” operate (above “return“) to destructure the handle and join a brand new consumer:
const { handle, isConnected } = useAccount();
const { join } = useConnect({
connector: new MetaMaskConnector(),
});
Notice: The “App.js” and “Header.js” strains of code supplied within the preliminary phases of this tutorial already embody these variables, so your scripts needs to be so as. In case you desire a extra detailed code walkthrough behind the “Join” button performance, watch the video on the high, beginning at 57:25.
After tweaking “App.js”, the “Join” button triggers MetaMask:
Including the Alternate Performance through the 1inch Aggregator
At this level, your decentralized change is ready to authenticate customers and join their MetaMask wallets, enable customers to pick tokens, and supply token quantities. Nonetheless, it’s not but capable of execute the precise change of tokens. So as to add this last piece of the “learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change” puzzle, you’ll want to implement the 1inch aggregator.

Primarily, you simply want so as to add the 1inch API endpoints offered within the introduction to “Swap.js”. All in all, under are the strains of code that you’ll want to add to “Swap.js”:
Import wagmi hooks below the present imports:import { useSendTransaction, useWaitForTransaction } from “wagmi”; Contained in the “Swap” operate, add “props” :operate Swap(props) {
const { handle, isConnected } = props; Add new state variables that may retailer transaction particulars and look ahead to transactions to undergo: const [txDetails, setTxDetails] = useState({
to:null,
information: null,
worth: null,
});
const {information, sendTransaction} = useSendTransaction({
request: {
from: handle,
to: String(txDetails.to),
information: String(txDetails.information),
worth: String(txDetails.worth),
}
})
const { isLoading, isSuccess } = useWaitForTransaction({
hash: information?.hash,
}) Under the “fetchPrices” operate, add the “fetchDexSwap” async operate: async operate fetchDexSwap(){
const allowance = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/approve/allowance?tokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}&walletAddress=${handle}`)
if(allowance.information.allowance === “0”){
const approve = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/approve/transaction?tokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}`)
setTxDetails(approve.information);
console.log(“not accepted”)
return
}
const tx = await axios.get(`https://api.1inch.io/v5.0/1/swap?fromTokenAddress=${tokenOne.handle}&toTokenAddress=${tokenTwo.handle}&quantity=${tokenOneAmount.padEnd(tokenOne.decimals+tokenOneAmount.size, ‘0’)}&fromAddress=${handle}&slippage=${slippage}`)
let decimals = Quantity(`1E${tokenTwo.decimals}`)
setTokenTwoAmount((Quantity(tx.information.toTokenAmount)/decimals).toFixed(2));
setTxDetails(tx.information.tx);
}
Notice: If you happen to want to discover ways to receive the above 1inch API hyperlinks from the “Swagger” part of the 1inch documentation, use the video on the high (1:09:10).
Lastly, add three “useEffect” capabilities under the present “useEffect“. They’ll cowl transaction particulars and pending transactions: useEffect(()=>{
if(txDetails.to && isConnected){
sendTransaction();
}
}, [txDetails])
useEffect(()=>{
messageApi.destroy();
if(isLoading){
messageApi.open({
sort: ‘loading’,
content material: ‘Transaction is Pending…’,
period: 0,
})
}
},[isLoading])
useEffect(()=>{
messageApi.destroy();
if(isSuccess){
messageApi.open({
sort: ‘success’,
content material: ‘Transaction Profitable’,
period: 1.5,
})
}else if(txDetails.to){
messageApi.open({
sort: ‘error’,
content material: ‘Transaction Failed’,
period: 1.50,
})
}
},[isSuccess])
Notice: You possibly can entry the ultimate “Swap.js” script on GitHub.
Fundamentals of Constructing a Decentralized Alternate for Cryptocurrency
Understanding the idea about decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges and the instruments to construct them is on no account a should. In any case, you may need already constructed your individual decentralized change following the above tutorial with out a extra profound data of the idea. Nonetheless, in the event you want to study what decentralized exchanges are, how they work, how they evaluate to centralized exchanges, and the gist of the instruments to construct a decentralized change for crypto, dive into the next sections.

What’s a Decentralized Alternate?
A decentralized change (DEX) is a peer-to-peer market the place customers get to commerce cryptocurrency with none middlemen. Most of these exchanges are decentralized as a result of there’s no central entity concerned and, thus, no single level of failure. In any case, the backends of DEXs exist on the blockchain. So, because of decentralized exchanges, we will execute monetary transactions with out banks, brokers, cost processors, or another sort of conventional middleman.
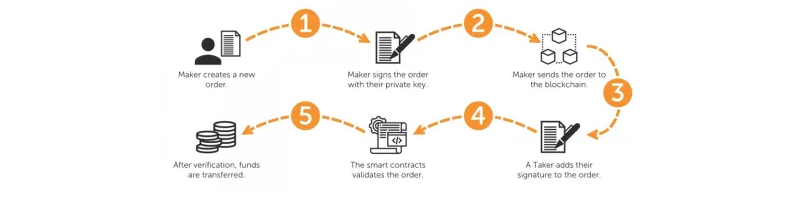
How Does a Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate Work?
DEXs’ choices and levels of decentralization might fluctuate; nevertheless, sensible contracts are the core tech behind their clear and trustless operations. A decentralized change depends on “liquidity swimming pools” – stacks of cryptocurrency belongings that sit beneath the change’s floor. So, ample liquidity swimming pools are required to satisfy purchase or promote orders. The belongings within the liquidity swimming pools come from buyers, who revenue from transaction charges charged to “pooling” customers.
When utilizing a decentralized cryptocurrency change, customers want to attach their Web3 wallets, resembling MetaMask. This permits them to be in full management of their belongings. As soon as linked, customers can change their belongings, put money into liquidity swimming pools, and carry out different DeFi (decentralized finance) actions. The precise choices fluctuate; nevertheless, the only choices are DEXs with token swaps, similar to the one you had an opportunity to construct within the above tutorial.
The important thing parts to safe exchanging of belongings with out intermediates are sensible contracts. These on-chain items of software program are programmed to mechanically execute predefined actions when particular predefined circumstances are met. As such, transactions both undergo or are reverted. It’s vital to notice that token swaps contain on-chain transactions. Consequently, customers must cowl the transaction fuel charges, which fluctuate relying on the blockchain community and present demand.
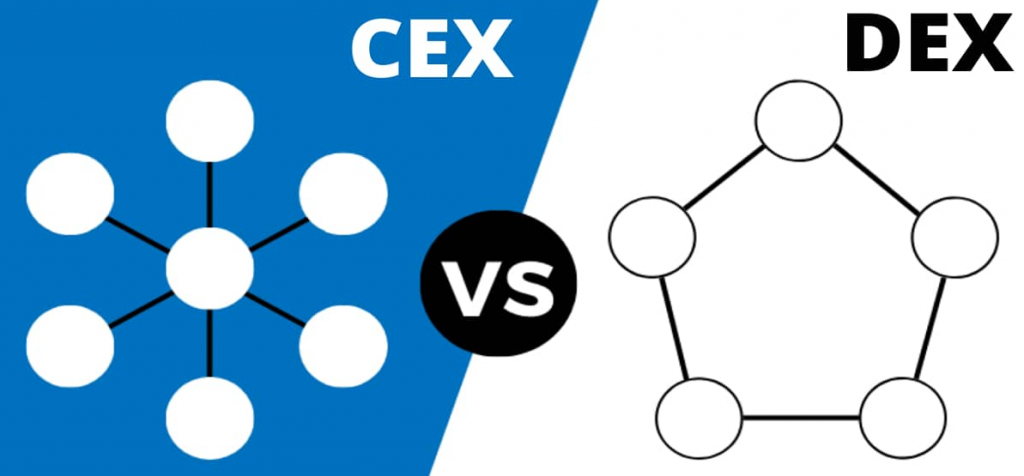
Decentralized vs Centralized Alternate
The next record outlines the primary variations between DEXs and CEXs:
Decentralization: CEXs: Operated by centralized organizations.DEXs: Operated by customers and liquidity suppliers – no central authority and management. Custody of belongings: CEXs: The change totally controls entry to crypto belongings. DEXs: Customers have unique management over their belongings. Impermanent loss: CEXs: No issues of impermanent loss on account of excessive liquidity.DEXs: Impermanent loss is a extremely attainable threat within the occasion of market fluctuations. Laws: CEXs: Regulated – not nameless.DEXs: No KYC and AML requirements – nameless. Liquidity: CEXs: Institutional buyers and a big consumer base guarantee greater liquidity.DEXs: Lack of regulatory requirements and competitors from CEXs scale back liquidity. Buying and selling choices: CEXs: Superior instruments – a number of buying and selling choices, together with spot buying and selling, futures buying and selling, and others. DEXs: Primary options – typically restricted to swaps, crypto lending and borrowing, and speculative investments; nevertheless, DEXs are evolving, and new buying and selling choices are launched typically. Safety: CEXs: Higher threat of hacks and server downtime.DEXs: Decrease safety dangers. Comfort: CEXs: Straightforward to make use of.DEXs: It may be tough for newcomers. Supply of funding: CEXs: Banks and bank cards.DEXs: Crypto wallets (e.g., MetaMask). Buying and selling: CEXs: Order guide through a centralized middleman.DEXs: Peer-to-peer buying and selling primarily based on an automatic market maker. Tradable tokens: CEXs: Restricted picks of tokens.DEXs: Quite a few choices.
Instruments to Construct a Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate
If you happen to additional discover learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change, you’ll study that the above-covered tutorial isn’t the one approach. As such, the instruments required to construct a DEX additionally fluctuate. Nonetheless, in relation to constructing a neat-looking and totally useful DEX with minimal effort, the strategy outlined herein is the best way to go. In that case, you want the next instruments to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change:
JavaScript: ReactJS framework to cowl the frontend.NodeJS framework to cowl the backend. The Moralis Web3 API to fetch on-chain information.The 1inch aggregator to implement the change options. Axios to effortlessly bridge the information from the backend to the frontend.The wagmi library to simply implement Web3 authentication. CSS for frontend styling.MataMask to hook up with your DEX and check its functionalities.You want testnet crypto taps to get testnet cryptocurrencies and check your DEX with none precise value (e.g., a Goerli faucet, Mumbai faucet, BNB faucet, Aptos testnet faucet, and so forth.).
After all, in the event you want to construct extra superior decentralized exchanges and even perhaps introduce some distinctive on-chain performance, you’ll want different Ethereum growth instruments. In that case, you’ll additionally need to study sensible contract programming and sensible contract safety. You might also be enthusiastic about changing your NodeJS backend with Python, wherein case you must discover “Web3 Python” choices.
Now, in the event you want to steer away from Ethereum and EVM-compatible chains and, as an example, deal with Solana, studying about Solana blockchain app growth and associated instruments is a should.
Easy methods to Construct a Decentralized Cryptocurrency Alternate – Abstract
In at present’s article, you realized learn how to construct a decentralized cryptocurrency change. As such, you have been capable of make the most of your JavaScript proficiency and mix it with the facility of Moralis and the 1inch aggregator to construct a neat DEX. Within the sections above, you additionally had a possibility to study the fundamentals of decentralized exchanges.
DEXs are simply one of many numerous dapps you may construct with the best instruments. Actually, utilizing JavaScript and the Moralis JS SDK offers you almost limitless choices concerning blockchain app growth round current sensible contracts. Apart from the Moralis Web3 Information API, Moralis gives many enterprise blockchain options. As an example, you may hearken to any pockets and sensible contract handle with the Moralis Streams API. The latter is a superior Notify API different that makes Web3 libraries out of date in some ways. One other wonderful instrument is its IPFS API – you may study extra about it in our IPFS Ethereum tutorial. If you happen to want to mint NFT from contract, you’ll need to get your gwei to ETH (and vice versa) conversion proper when overlaying transaction charges.
To study extra about dapp growth with Moralis, be sure that to discover the Moralis documentation, Moralis YouTube channel, and Moralis weblog. With these assets, you may develop into a Web3 developer without cost. Nonetheless, in the event you want to take a extra skilled method to your blockchain growth schooling, think about enrolling in Moralis Academy.
[ad_2]
Source link





